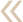
The zygomatic bone is one of the "puzzles" that make up the facial skeleton. It usually breaks in the area of the connection with the adjacent bones. This area is presented by so-called sutures: zygo-frontal, zygo-maxillary, zygo-temporal.
Fracture of the zygomatic complex occurs when the area of the zygomatic elevation (the most prominent point under the eye) is hit.
Most often, the zygomatic complex suffers during an attack, an accident (especially for not fastened passengers in the back seats), after a fall from height.
Fracture classification
In injuries, damage most often occurs not only to the zygomatic, but also to the adjacent bones. Thus, we are dealing with fractures of the zygomatic, nasal, orbital and maxillary complex in different variations. The only type of fracture within the zygomatic bone solely is the so-called isolated fracture of the zygomatic arch.
What characterizes damage?
After injury occur the following:
-
pain,
-
swelling,
-
deformation of the injury area,
-
numbness of the skin of the infraorbital region and the teeth of the upper jaw on the side of the lesion,
-
nose bleeding on the side of injury,
-
restriction of opening and lateral movements of the mandible,
-
pain when chewing.
First aid:
-
Apply cold to the place of injury. This may be a pack with ice wrapped in a towel.
-
If there is a wound, treat it with an aqueous antiseptic (Miramistin, chlorhexidine) and apply a bandage.
-
If the pain is severe, take pain medication.
-
Adress to the clinic where a doctor will examine you and prescribe additional investigations. These may be a radiograph or computed tomography.
Diagnosing
The “gold standard” in the diagnosis of injuries of the facial skeleton is computed tomography, that allows to perform the cuts with a minimal interval of 0.5-1 mm.
Malar bone fracture treatment
Fractures without displacement and dysfunction are treated conservatively and do not require hospitalization. In this case, patients are recommended to:
-
exclude products for 10-14 days that require chewing, because the chewing muscle is attached partially to the temporal bone and may cause displacement of fragments;
-
apply ointments and lotions that reduce swelling;
-
take analgetics in case of pain.
Fractures with displaced fragments require surgical treatment.
Surgical treatment methods
Surgical treatment of zygomatic fractures were being developed particularly actively in the second half of the 20th century. Many authors offered their methods of access to the zygomatic bone and its reposition: techniques of Limberg, Kazanian, Dubov, Duchant ...
For the sake of justice, we should note that that we still use one of the methods named by its author. This is the Limberg technique, which is however applied only in case of isolated fractures of the zygomatic arch, which do not require additional fixation after reposition.
With the introduction of computed tomography into widespread practice, it has become possible to get a “map” of fracture lines before the operation, and modern technical capabilities and principles of osteosynthesis joined all existing methods into one.
The surgery performed by this method is aimed at repositioning (putting in the correct position, matching) fragments and fixing them with titanium microplates. Plates are placed on the bone through micro incisions. According to modern principles for the stable fixation of the zygomatic bone, at least 3 following points of fixation of the fragments are necessary: in the region of the lower orbital margin, the zygo-frontal suture and the zygo-alveolar crest.
The resulting duration of rehabilitation has decreased. The hospital stay is from 1 to 3 days. Usually control computed tomography scan is performed on the day after the surgery, and if there are no complications, the patient is discharged.
Patients return to normal life in 7-10 days; however, sauna, swimming pool, contact sports, hypothermia are not recommended during up to one month.
Consequences of the malar bone fracture
Fracture with displacement of fragments can lead to deformation of the face and impaired chewing function.
Complications arising after a fracture of the zygomatic bone
On the part of the paranasal sinuses: maxillary sinusitis.
On the part of the eye: enophthalmos, hypophthalmos, double vision.
Prolonged numbness of the teeth of the upper jaw and the skin of the infraorbital region.
Restriction of mouth opening, lateral movements of the jaw, which cause difficulties when eating.
Author: Alexey Lobkov, maxillofacial surgeon, otorhinolaryngologist

 Write to WhatsApp
Write to WhatsApp.webp)